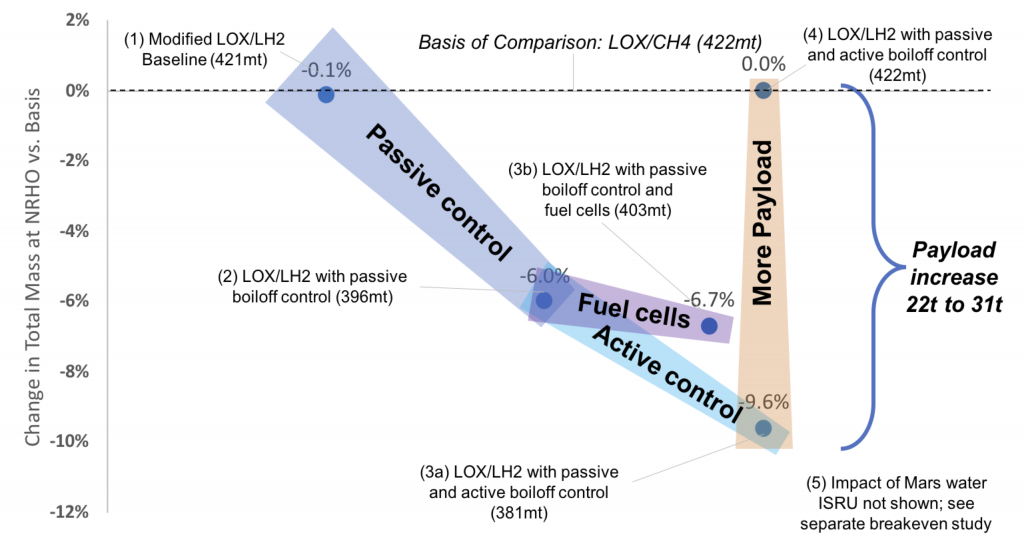
Lunar Lander Extensibility – Blue Origin
This project, sponsored by the Aerospace Corporation, focuses on the design and optimization of a responsive constellation of satellites, which may move between Global Observation Mode and Regional Observation Mode in response to events of interest. By allowing satellites to maneuver on-demand, high revisit frequencies may be achieved to cover a changing target location over the constellation’s lifetime. Current areas of work include adapting this constellation design to track mobile targets such as hurricanes, integrating low thrust maneuver capability, and understanding how this constellation’s performance and cost may compare to other mission architectures like responsive launch.